Introduction
GPRS Tunneling protocol is an important IP/UDP based protocol used in GSM, UMTS and LTE core networks. It is used to encapsulate user data when passing through core network and also carries bearer specific signalling traffic between various core network entities. This protocol has several advantages which will be discussed later.GPRS Tunneling Protocol Types
Why is GTP used in LTE?
- It provides mobility. When UE is mobile, the IP address remains same and packets are still forwarded since tunneling is provided between PGW and eNB via SGW
- Multiple tunnels (bearers) can be used by same UE to obtain different network QoS
- Main IP remains hidden so it provides security as well
- Creation, deletion and modification of tunnels in case of GTP-C
GTP Interfaces in LTE
In LTE, version 2 is used for GTP-C and version 1 is used for GTP-U
How GTP-U Works ?
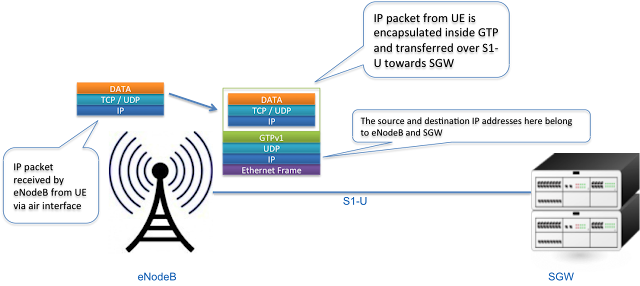
GTP-U encapsulation of UE user plane traffic can be easily understood by taking any simple example. Lets see what happens when IP packet generated by UE reaches to eNodeB and is then forwarded to SGW.Consider any application on UE creates an IP/TCP packet. This packet consist of actual data by application, TCP or UDP header and then IP field information which has source address of UE and destination address of application server (e.g. Facebook)
When the eNodeB receives this packet over air interface, it will put the IP packet inside GTP header which has information related to tunnel IDs. Then further, it is encapsulated inside UDP and IP header and forwarded as ethernet frame towards SGW. Here the IP header contains eNodeB IP as a source address and SGW IP as a destination address
GTP-C signalling messages
As GTP-Cv2 in LTE is used for tunnel management, some of the signalling messages are listed below which use GTP-Cv2 protocol
Please check Table 6.1-1(3GPP TS 29.274) for more detailed list of GTP-C based messages.