Background: Why we need QoS ?
There are premium subscribers who always want to have better user experience on their 4G LTE device. These users are willing to pay more for high bandwidth and better network access on their devices. Not only the subscribers but some services itself need better priority handling in the network (e.g. VoIP call). To be able to full fill this, QOS plays the key role. QOS defines priorities for certain customers / services during the time of high congestion in the network3GPP definition for QoS
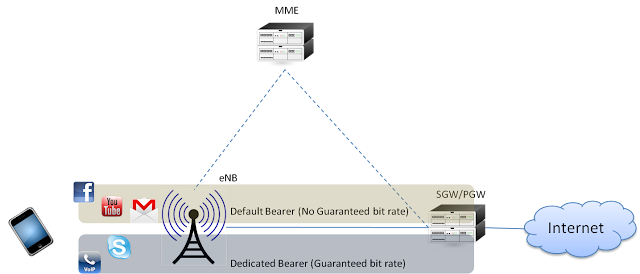
In LTE Network QoS is implemented between UE and PDN Gateway and is applied to a set of bearers. 'Bearer' is basically a virtual concept and is a set of network configuration to provide special treatment to set of traffic e.g. VoIP packets are prioritized by network compared to web browser traffic.
In LTE, QoS is applied on Radio bearer, S1 bearer and S5/S8 bearer, collectively called as EPS bearer as shown in figure below.
In LTE, QoS is applied on Radio bearer, S1 bearer and S5/S8 bearer, collectively called as EPS bearer as shown in figure below.
In order to comprehend the concept of QoS , we must understand the bearer types and properties associated with each bearer through hierarchical chart as shown below. First there are two types of Bearer, i.e. Dedicated bearer and Default bearer. There is at-least one default bearer established when UE is attached to LTE network while dedicated bearer is always established when there is need to provide QoS to specific service (like VoIP, video etc). Please go through the article Default and Dedicated Bearer which hopefully will help to explain the concept in more detail.
Dedicated bearer can be subdivided into Non-GBR and GBR types.
GBR provides guaranteed bit rate and is associated with parameters like GBR and MBR
- GBR: The minimum guaranteed bit rate per EPS bearer. Specified independently for uplink and downlink
- MBR: The maximum guaranteed bit rate per EPS bearer. Specified independently for uplink and downlink
On the other hand, Non-GBR bearer does not provide guaranteed bit rate and has parameter like A- AMBR and UE- AMBR
- A-AMBR: APN Aggregate maximum bit rate is the maximum allowed total non-GBR throughput to specific APN. It is specified interdependently for uplink an downlink
- UE -AMBR: UE Aggregate maximum bit rate is the maximum allowed total non-GBR throughput among all APN to a specific UE
As you can see, the default bearer can only be non-GBR type. Some other important terms associated with each bearer type are discussed below:
- ARP: Allocation and retention priority is basically used for deciding whether new bearer modification or establishment request should be accepted considering the current resource situation.
- TFT: Traffic flow template is always associated with dedicated bearer and while default bearer may or may not have TFT. As mentioned earlier, dedicated bearer provides QoS to special service or application and TFT defines rules so that UE and Network knows which IP packet should be sent on particular dedicated bearer. It usually has rules on the basis of IP packet destination/source or protocol used.
L-EBI: It stands for Linked EPS bearer ID. As I discussed in previous article about dedicated and default bearer, we know that each dedicated bearer is always linked to one of default bearers. L-EBI tells Dedicated bearer which default bearer it is attached to.
IP Address/ PDN: Each default bearer is attached to some PDN network and has its own IP address while dedicated bearer does not need this since it is linked to default bearer.
You can also see one other parameter associated with all bearers i.e. QoS class of identifier (QCI).This parameter basically defines IP level packets characteristics as shown below
EXAMPLE
Let me try to explain here again with the same example I gave in Default and Dedicated Bearer section
Usually LTE networks with VoLTE implementations have two default and one dedicated bearer
Default bearer 1: Used for signaling messages (sip signaling) related to IMS network. It uses qci 5
Dedicated bearer: Used for VoLTE VoIP traffic. It uses qci 1 and is linked to default bearer 1
Default bearer 2: Used for all other smartphone traffic (video, chat, email, browser etc), assuming qci 9 is used here
This means that Default bearer 1 is associated with IMS PDN and has specific IP address. It has throughput limitations defined in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR. Since it has qci 5 which means that its IP packets has the highest priority over other IP packets and maximum delay as 100ms between UE and PGW with packet loss percentage up to 10-6
Default bearer 2 is associated with internet PDN and has specific IP. It has throughput limitations defined in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR as well. Since it has qci 9 which means that its IP packets has the lowest priority over other IP packets and maximum delay possible as 300ms between UE and PGW with packet loss percentage up to 10-6
Dedicated bearer will be linked to Default bearer 1 with L-EBI and it also has TFT which basically defines which IP packets should be allowed to travel on this bearer. It has throughput limitations defined in terms of MBR and GBR. Since it is using QCI 1, the IP packets traveling on this bearer have the second highest priority. The maximum delay possible to IP packets on this bearer is 100 ms and the percentage of packet loss will be under 10-2